This post is automatically translated with LLM. The translation content has NOT been reviewed and may contain errors.
- Is it 9102 already?
- Yes, it is.
Why Do This
I have a Raspberry Pi 3B and an ASUS Tinker Board. Sometimes issues like Wi-Fi failures/configuration errors/pacman -Syu system breakage might cause one board to lose network connection. By connecting the serial ports of both boards and establishing a dial-up network connection, I can SSH into the problematic board from the other one when Wi-Fi or Ethernet fails.
(Also, if you buy a Raspberry Pi without tinkering with GPIO, you might as well get an x86 Atom mini PC instead)
How to Set Up
Hardware Setup:
Connect the serial ports of both boards. The Raspberry Pi's serial port uses Pin 8 (TX) for transmission and Pin 10 (RX) for reception (check pinout.xyz). The Tinker Board's serial port also uses Pin 8 (TX) and Pin 10 (RX). Use two jumper wires to connect:
- Raspberry Pi Pin 8 → Tinker Board Pin 10
- Raspberry Pi Pin 10 → Tinker Board Pin 8

If the boards use separate power supplies (like mine), connect a third jumper wire between their GND pins (Pin 6 on both boards). This ensures a common ground reference for voltage level consistency.
Software Setup:
Install pppd on both devices:
# Debian-based (Tinker Board)
apt-get install ppp
# Arch-based (Raspberry Pi)
pacman -S pppStart pppd services:
# Run on one board
pppd -detach noauth /dev/ttyS1 1000000 172.18.233.1:172.18.233.2 local nocrtscts xonxoff
# Run on the other board
pppd -detach noauth /dev/ttyS1 1000000 172.18.233.2:172.18.233.1 local nocrtscts xonxoffParameter Explanation:
-detach: Keep process in foregroundnoauth: Disable authentication/dev/ttyS1: Serial device path (default for RPi 3B & Tinker Board)1000000: Baud rate (tested maximum stable speed)172.18.233.1:172.18.233.2: Local IP : Peer IPlocal: Disable modem control linesnocrtscts: Disable hardware flow controlxonxoff: Enable software flow control
Now you can ping between both boards.
Performance
At 1,000,000 baud rate:
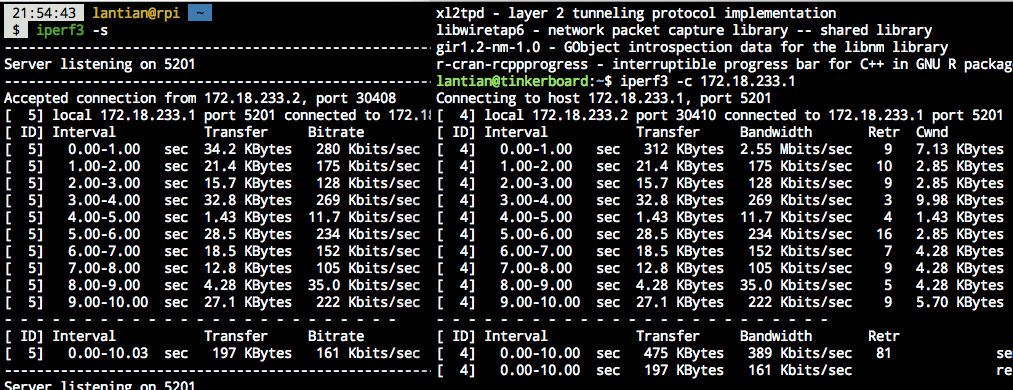
Well... just enough for SSH usage.