This post is automatically translated with LLM. The translation content has NOT been reviewed and may contain errors.
NAT64 is a technology that emerged during the transition from IPv4 to IPv6. It allows IPv6-only devices to access IPv4 networks by mapping IPv4 addresses to a specific IPv6 address range. However, since purely IPv6-capable devices are still uncommon, its current applications in China mainly focus on two areas:
- For educational network users where IPv4 is charged/rate-limited/volume-capped while IPv6 is free/unlimited, public NAT64 services can help save costs.
- For iOS app developers, it serves as a testing environment to pass App Store review requirements.
We can also set up a NAT64 server on our own router with both IPv4 and IPv6 connectivity by installing appropriate software. Common solutions include Tayga and Jool. Tayga is outdated with its last update dating back to 2011, while Jool remains actively maintained. Therefore, this guide uses Jool for setup.
Installing Jool
The first step is installing Jool. Arch Linux users can find Jool in AUR, but it's unavailable in Debian/Ubuntu official repositories, requiring manual compilation on these systems.
For Arch Linux:
Simply run yaourt -S jool-dkms-git. Raspberry Pi users need to modify the PKGBUILD by changing arch=('i686' 'x86_64') to arch=('i686' 'x86_64' 'armv7h') to add ARM architecture support. After installation, proceed from the "Set kernel module auto-load at boot" step below.
For Debian/Ubuntu:
# Install dependencies
apt-get install build-essential dkms autoconf automake linux-headers
# Download Jool (latest version 3.5.6 at time of writing)
wget https://github.com/NICMx/releases/raw/master/Jool/Jool-3.5.6.zip
unzip Jool-3.5.6.zip
cd Jool-3.5.6
# Install kernel module
dkms install .
# Install management tools (optional)
cd usr
./configure && make && make install
# Set kernel module auto-load at boot
cat >/etc/modprobe.d/jool.conf <<EOF
options jool pool6=64:ff9b::/96
EOF
echo jool > /etc/modules-load.d/jool.conf
# Load kernel module
modprobe -v jool pool6=64:ff9b::/96After installation, run jool. If you see output similar to Status: Enabled, the installation succeeded.
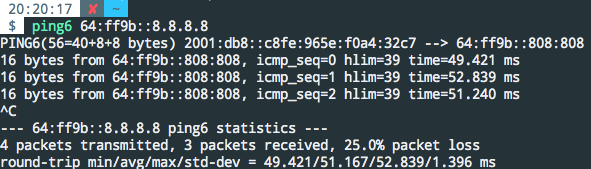
Testing NAT64
The IPv6 address space reserves a specific pool for NAT64: 64:ff9b::/96 as shown above. You can access IPv4 resources by appending the IPv4 address to this prefix. For example, to access 8.8.8.8, use 64:ff9b::8.8.8.8.
Note: Direct access to this address from the Jool host machine will fail. You must configure the host as a router and access it from another device. I successfully tested this by setting up a Raspberry Pi as a WiFi hotspot router and pinging the address from a connected computer.